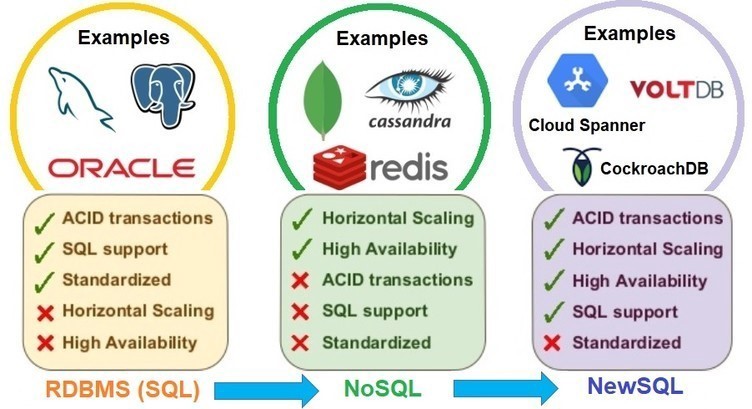
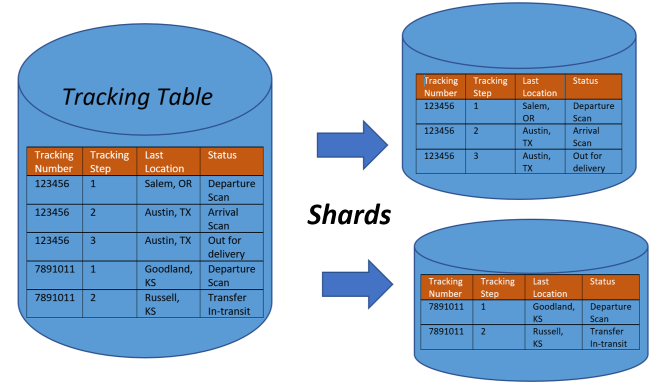
This PostgreSQL ecosystem , showcasing various extensions and tools categorized by functionality. PostgreSQL is a powerful open-source relational database system, and this diagram illustrates how its extensibility allows integration with various technologies. Let’s break it down:
1. Core – PostgreSQL
At the center is the PostgreSQL, representing the database itself, which serves as the foundation for all the extensions and tools depicted around it.
2. Categories of Extensions & Tools
The surrounding sections categorize various PostgreSQL extensions, plugins, and related tools based on their purpose.
A. Time-Series & Temporal Data (Top-Center)
- TimescaleDB: A popular PostgreSQL extension for time-series data.
- pg_timeseries, pg_timetable: Extensions for managing time-series workloads.
- temporal_tables, table_version: Used for maintaining historical records and time-based versioning.
- e-maj: Supports auditing and versioning of database tables.
B. AI, Machine Learning & Vector Search (Top-Right)
- PGVector: Supports vector similarity search, commonly used in AI applications.
- pgai, pg_tiktoken: Integrates AI and tokenization functionalities.
- MADlib: A library for scalable in-database machine learning.
- PostgresML: An ML framework designed for PostgreSQL.
C. OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) & Analytics (Right-Center)
- Citus: A PostgreSQL extension for distributed and scalable OLAP.
- pg_duckdb: Enables PostgreSQL to interact with DuckDB, a fast in-memory analytics database.
- pg_parquet: Supports reading Parquet files in PostgreSQL.
- pg_strom, HYDRA: Accelerate analytical queries using GPU processing.
D. Procedural Languages (Bottom-Right)
- Allows PostgreSQL to support multiple programming languages, such as:
- PL/pgSQL, PL/Tcl, PL/Python, PL/R, PL/Perl, PL/Java, PL/Prolog, PL/Haskell, PL/Rust.
E. Geospatial Extensions (Bottom-Center)
- PostGIS: The most popular geospatial database extension for PostgreSQL.
- pg_geohash, pg_routing: Tools for spatial indexing and route calculations.
- H3, GISWater: Additional geospatial processing tools.
F. Full-Text Search (Bottom-Left)
- pg_trgm, pg_bigm: Enables fuzzy and bigram-based text searches.
- pgroonga, ZomboDB: Full-text search integrations with PostgreSQL.
- zhparser, hunspell: Language processing extensions.
G. Featured Extensions & Performance Tools (Left-Center)
- HypoPG: Creates hypothetical indexes to analyze query performance.
- jsonschema: Supports JSON schema validation in PostgreSQL.
- pg_hint_plan, plan_filter: Query optimization tools.
H. Foreign Data Wrappers (FDW) & External Database Connections (Top-Left)
- FDW (Foreign Data Wrappers): Enables PostgreSQL to interact with other databases like:
- MongoDB, MySQL, SQLite, Oracle, SQL Server, Parquet, DuckDB.
- Multicorn: A Python-based FDW framework.

3. Summary
This diagram effectively visualizes PostgreSQL’s extensibility, covering:
- Time-series (TimescaleDB)
- AI & Machine Learning (PGVector, PostgresML)
- OLAP & Analytics (Citus, DuckDB, Parquet)
- Geospatial Data (PostGIS)
- Full-Text Search (pg_trgm, pgroonga)
- External Database Integration (FDW, Multicorn)
- Programming Language Support (PL/Python, PL/Rust, PL/pgSQL)
This ecosystem makes PostgreSQL a versatile and powerful database solution for various domains, including AI, analytics, geospatial data, and high-performance computing.