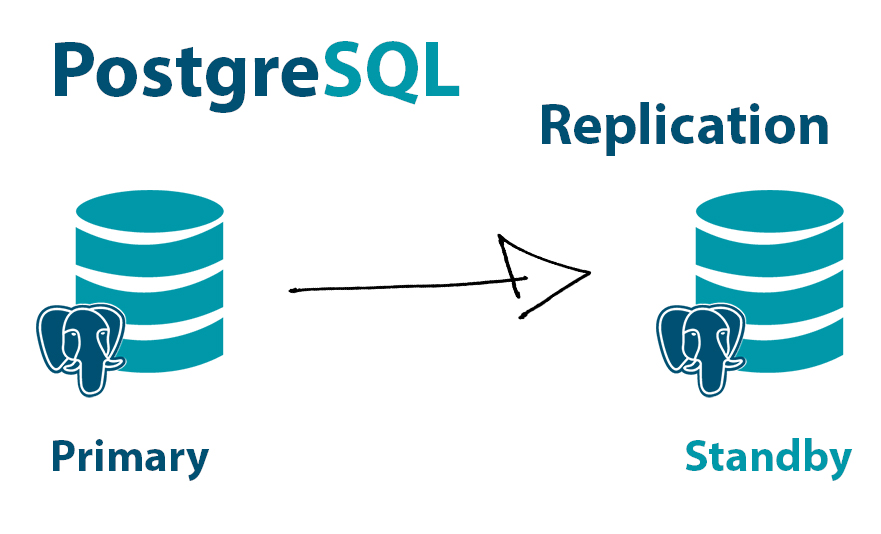
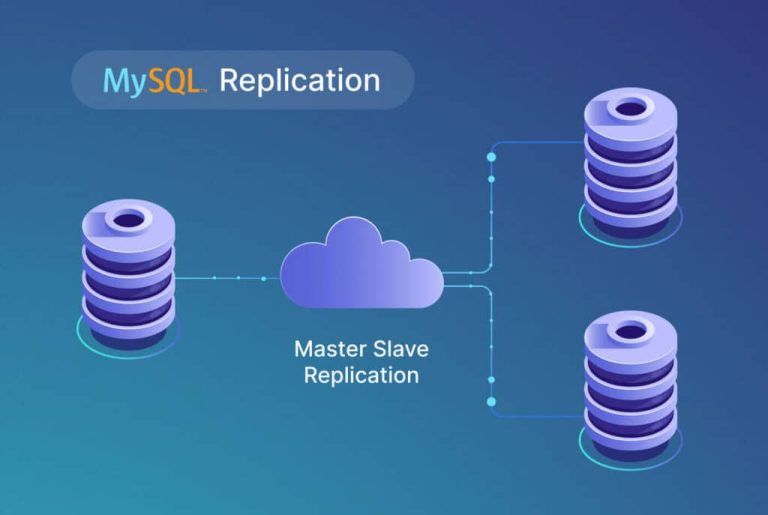
PostgreSQL, with its robust support for replication, is a popular choice for building scalable and fault-tolerant databases. In this article, we’ll explore how to use Docker-Compose to set up a PostgreSQL master-slave replication configuration and connect a Laravel application to this database cluster.
Docker-Compose Configuration
Start by creating a project directory and organizing it with the following structure:
postgres-replication/ |-- master/ | |-- Dockerfile | |-- postgresql.conf | |-- pg_hba.conf |-- slave/ | |-- Dockerfile | |-- postgresql.conf | |-- pg_hba.conf |-- laravel/ | |-- (Laravel files) |-- docker-compose.yml
Docker-Compose Configuration
Create a docker-compose.yml file in the project root:
version: '3'
services:
master-db:
build:
context: ./master
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: master_user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: master_pass
POSTGRES_DB: laravel_db
ports:
- "5432:5432"
slave-db:
build:
context: ./slave
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: slave_user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: slave_pass
POSTGRES_DB: laravel_db
ports:
- "5433:5432"
depends_on:
- master-db
laravel-app:
build:
context: ./laravel
environment:
DB_CONNECTION: pgsql
DB_HOST: master-db
DB_PORT: 5432
DB_DATABASE: laravel_db
DB_USERNAME: master_user
DB_PASSWORD: master_pass
ports:
- "8000:8000"
depends_on:
- master-db
- slave-dbThis docker-compose.yml file defines three services: master-db, slave-db, and laravel-app. The master and slave database services are built from the respective Dockerfile configurations in the master and slave directories.
Dockerfile for PostgreSQL Master
Create a Dockerfile inside the master directory:
FROM postgres:latest COPY ./postgresql.conf /etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf COPY ./pg_hba.conf /etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf CMD ["postgres", "-c", "config_file=/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf"]
Dockerfile for PostgreSQL Slave
Create a Dockerfile inside the slave directory:
FROM postgres:latest COPY ./postgresql.conf /etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf COPY ./pg_hba.conf /etc/postgresql/pg_hba.conf CMD ["postgres", "-c", "config_file=/etc/postgresql/postgresql.conf", "-c", "hot_standby=on"]
PostgreSQL Configuration Files (For Both Master and Slave)
Create postgresql.conf and pg_hba.conf files inside the master and slave directories. Here’s a basic example; adjust as needed:
postgresql.conf:
# Master Configuration listen_addresses = '*' wal_level = replica max_wal_senders = 3 wal_keep_segments = 8 checkpoint_segments = 8 archive_mode = on archive_command = 'cp %p /var/lib/postgresql/data/archive/%f' # Slave Configuration hot_standby = off
pg_hba.conf:
# Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the # replication privilege. local replication all trust host replication all 127.0.0.1/32 trust host replication all ::1/128 trust
Connecting Laravel to PostgreSQL
Ensure your Laravel application is configured to use PostgreSQL as its database. Update the .env file in the laravel directory with the following settings:
DB_CONNECTION=pgsql DB_HOST=master-db DB_PORT=5432 DB_DATABASE=laravel_db DB_USERNAME=master_user DB_PASSWORD=master_pass
Running the Application
Navigate to the project root directory and execute:
docker-compose up --build
This command will build the necessary Docker images and start the containers for the PostgreSQL master, slave, and Laravel application.
Access the Laravel application at http://localhost:8000. The application will use the PostgreSQL master for read and write operations and the slave for read-only operations, creating a scalable and fault-tolerant database setup.
Conclusion
By leveraging Docker-Compose, you can easily orchestrate a PostgreSQL master-slave replication setup along with a Laravel application. This configuration allows for improved database performance, high availability, and fault tolerance. As your Laravel application scales, this PostgreSQL replication setup can be a crucial component in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your database operations. Adjust the configurations based on your specific requirements and continue building robust and scalable applications.