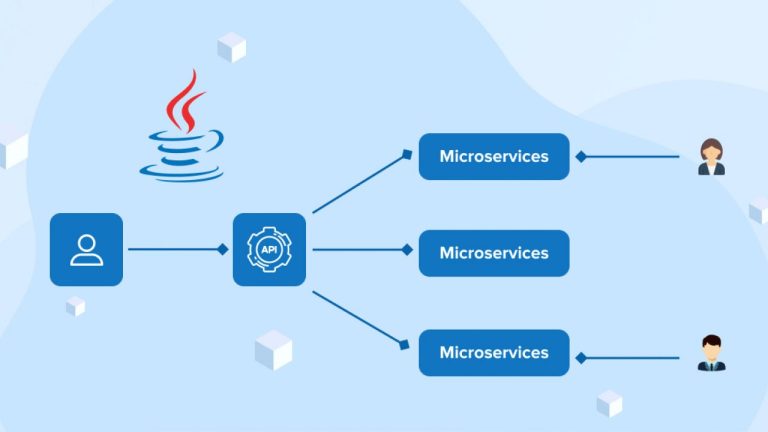
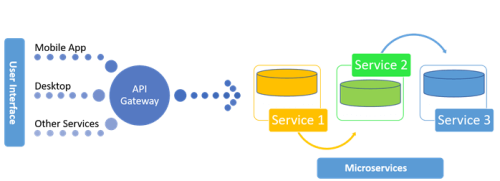
Below are simple examples of a microservice in C#, Java, and Golang. Keep in mind that microservices are typically part of a larger system and involve more complex functionality, but these examples aim to illustrate the basic structure.
C# Microservice:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Additional services can be configured here
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Microservice in C#");
});
}
} Java Microservice (Using Spring Boot):
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MicroserviceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MicroserviceApplication.class, args);
}
}
@RestController
class MicroserviceController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String hello() {
return "Microservice in Java";
}
}Golang (Go) Microservice:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprint(w, "Microservice in Golang")
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}These examples demonstrate the setup of a basic microservice using different languages and frameworks. Remember that real-world microservices would involve more complexity, including communication with databases, integration with other services, and proper error handling.