C# Microservices: Empowering Scalable and Modular Architectures
Introduction to C# microservice using ASP.NET Core
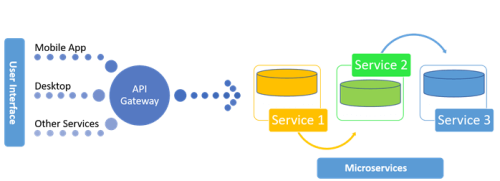
Microservices architecture has emerged as a pivotal paradigm in modern software development, promoting scalability, agility, and ease of maintenance. C# developers have embraced this approach, leveraging the language’s strengths to build robust and efficient microservices. In this article, we delve into the world of C# microservices, exploring their benefits, challenges, and practical implementation.
Key Characteristics of Microservices:
Microservices decompose applications into smaller, independently deployable services. Each microservice focuses on a specific business capability, communicates through well-defined APIs, and operates autonomously.
Advantages of C# for Microservices:
- Language Features: C# provides a rich set of features, including strong typing, asynchronous programming, and LINQ (Language Integrated Query), facilitating the creation of reliable and performant microservices.
- .NET Core: The advent of .NET Core has been a game-changer. It’s lightweight, cross-platform, and designed with microservices in mind, making it an ideal framework for C# microservices.
- Integration with Azure: Microsoft Azure offers a robust set of tools for microservices development. Azure Service Fabric, Azure Functions, and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) provide a scalable and managed environment for deploying and orchestrating microservices.
Implementation Patterns:
- RESTful APIs: Microservices communicate through RESTful APIs, and C# excels in building RESTful services. ASP.NET Core Web API is a popular choice for creating lightweight and efficient APIs.
- Message Queues: Asynchronous communication between microservices is crucial for scalability. C# supports message queues, with tools like Azure Service Bus or RabbitMQ, to enable seamless communication.
- Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes have become integral to microservices deployment. C# applications can be containerized, ensuring consistency across different environments.
Challenges and Best Practices:
- Data Consistency: Maintaining data consistency across microservices can be challenging. Developers often employ event sourcing or distributed transactions to address this concern.
- Service Discovery: Microservices need to discover and communicate with each other dynamically. Service discovery tools or platforms like Consul or Azure Service Discovery help manage this complexity.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing effective monitoring and logging is essential for identifying and resolving issues in a microservices architecture. Tools like Application Insights or ELK Stack aid in this aspect.
Simple C# microservice using ASP.NET Core
for a hypothetical “User Management” service. This microservice will expose RESTful APIs for managing user data.
// File: UserController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
[Route("api/users")]
[ApiController]
public class UserController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly List<User> _users;
public UserController()
{
// In a real-world scenario, you would interact with a database or another service.
_users = new List<User>
{
new User { Id = 1, Name = "John Doe", Email = "[email protected]" },
new User { Id = 2, Name = "Jane Doe", Email = "[email protected]" }
};
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<User>> GetUsers()
{
return Ok(_users);
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public ActionResult<User> GetUserById(int id)
{
var user = _users.Find(u => u.Id == id);
if (user == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(user);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult<User> CreateUser(User newUser)
{
// In a real-world scenario, you would handle data validation, storage, etc.
newUser.Id = _users.Count + 1;
_users.Add(newUser);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(GetUserById), new { id = newUser.Id }, newUser);
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public IActionResult UpdateUser(int id, User updatedUser)
{
var existingUser = _users.Find(u => u.Id == id);
if (existingUser == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
// In a real-world scenario, you would update user data.
existingUser.Name = updatedUser.Name;
existingUser.Email = updatedUser.Email;
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public IActionResult DeleteUser(int id)
{
var userToRemove = _users.Find(u => u.Id == id);
if (userToRemove == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_users.Remove(userToRemove);
return NoContent();
}
}
// User model class
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}This code defines a simple UserController with CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations for managing user data. Note that in a real-world scenario, you would likely use a database or another data storage solution and implement additional features such as authentication and authorization.
C# microservices have evolved into a robust and practical solution for building scalable and maintainable applications. Leveraging the strengths of the C# language, .NET Core framework, and Azure ecosystem, developers can navigate the challenges of microservices architecture while capitalizing on its numerous benefits. As organizations continue to embrace agility and scalability, C# microservices stand at the forefront, driving innovation in the dynamic landscape of software development.